Europa Nostra - Most Endangered 2023
On the occasion of the 10th anniversary of the 7 Most Endangered Programme in 2023, Europa Nostra – the European Voice of Civil Society Committed to Cultural and Natural Heritage – and the European Investment Bank Institute have just announced the 11 most threatened heritage sites in Europe shortlisted for this year’s edition of the programme.

Among 11 most endangered monuments and heritage sites in Europe for 2023 are Kortrijk Railway Station (Belgium), Domain and Royal Museum of Mariemont in Moralwez (Belgium), Tchakcinij Fortress in Zugdidi (Georgia), Sister's House Ensemble - former Moravian settlement in Kleinwelka (Germany), Mansion Konaki of Gidas in Alexandria (Greece), Herman Otto Museum in Miskolc (Hungary), Memento Park in Budapest (Hungary), Cultural Landscape of Paštrovska Gora (Montenegro), Cultural Landscape of Sveti Štefan in Paštroviči (Montenegro), Watermills of Bistrica in Petrovac na Mlavi (Serbia), and the Partisan Memorial Cemetery in Mostar (Bosnia and Herzegovina) designed by Bogdan Bogdanović.
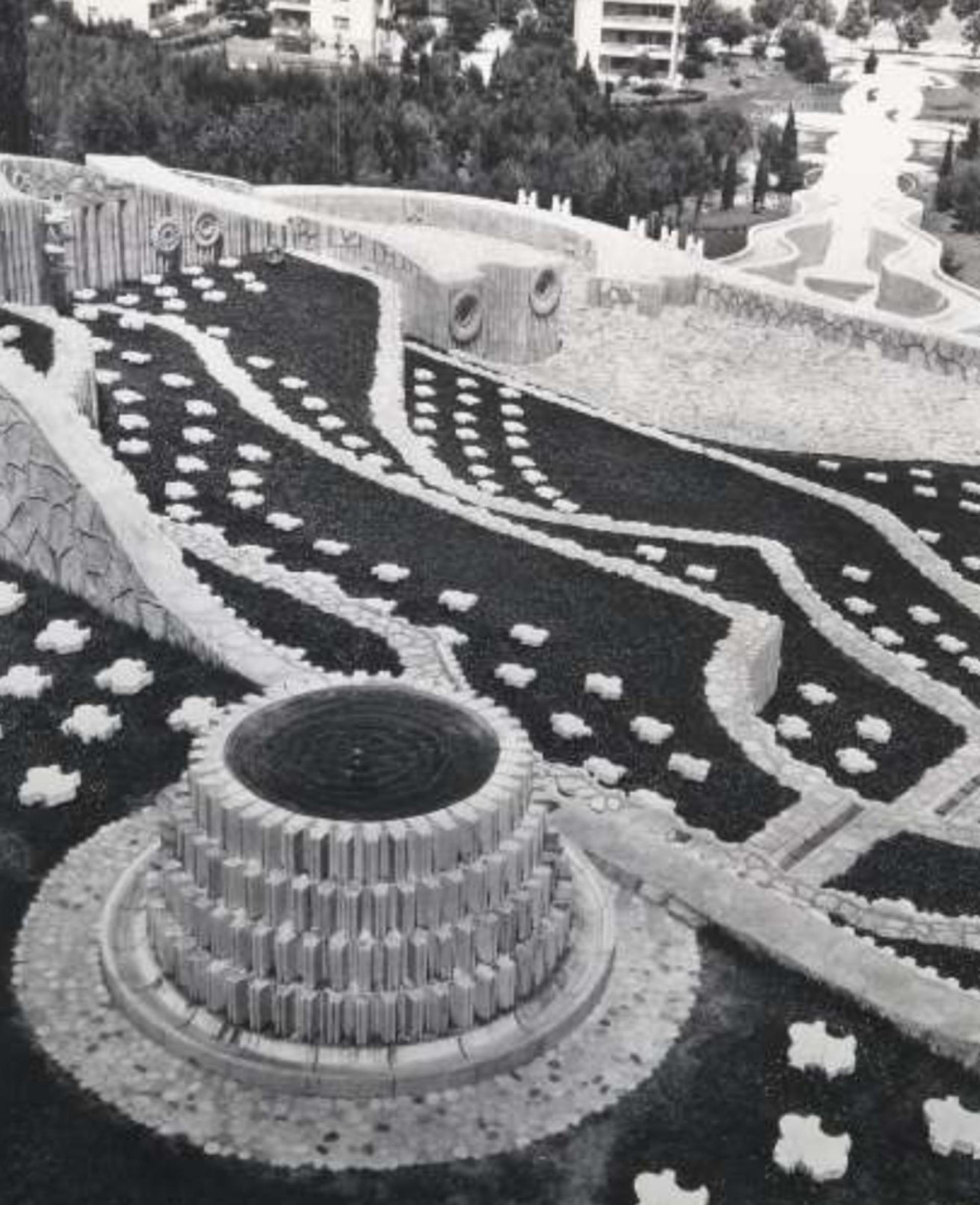

A view from the top of the cemetery before the latest conflicts.
The selection was made on the basis of the outstanding heritage significance and cultural value of each of the sites as well as on the basis of the serious danger that they are facing today. The level of engagement of local communities and the commitment of public and private stakeholders to saving these sites were considered as crucial added values. Another selection criterion was the potential of these sites to act as a catalyst for sustainable development and as a tool for promoting peace and dialogue within their localities and wider regions.
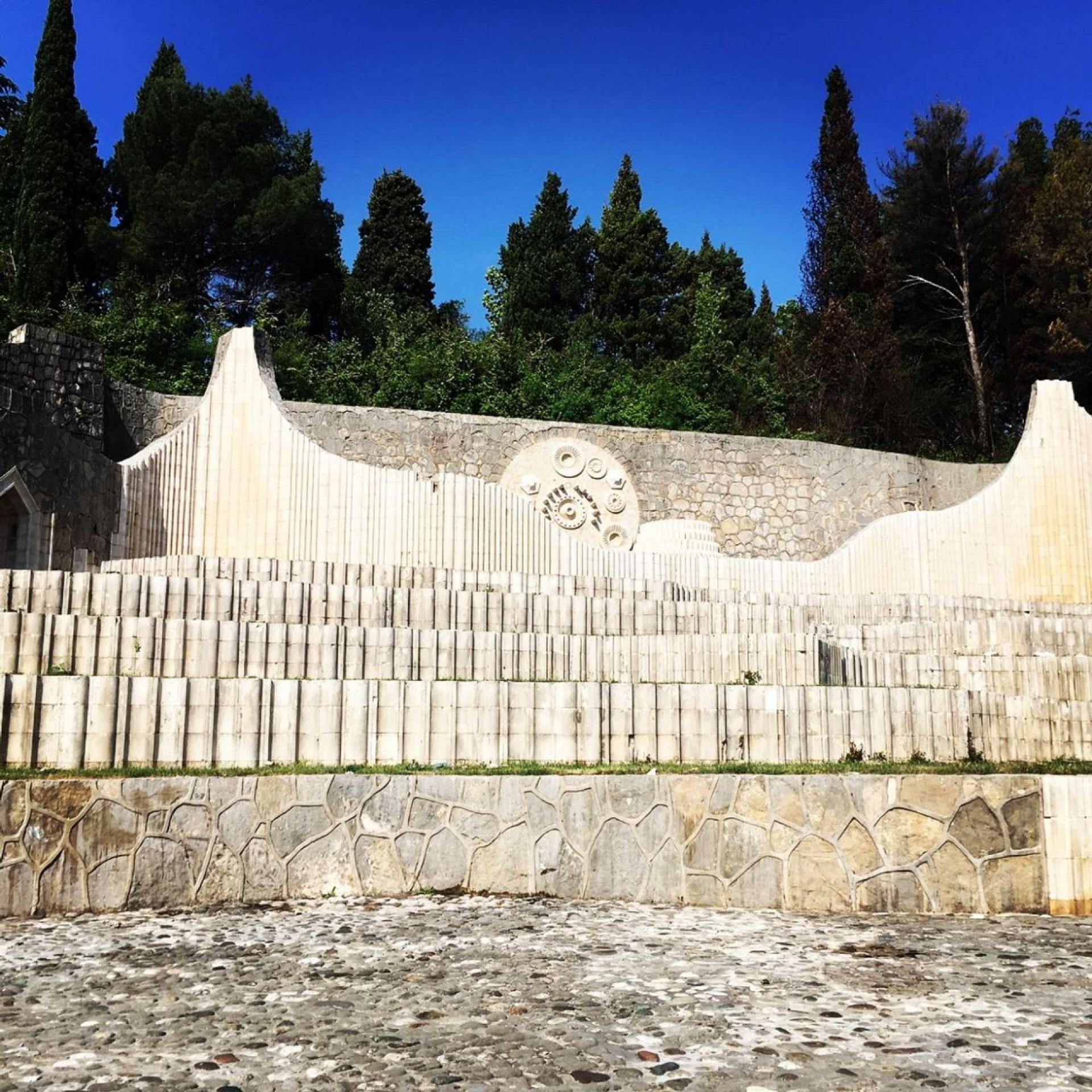

A view on the central fountain at the top of the site.
The 11 endangered heritage sites were shortlisted by an international Advisory Panel, comprising experts in history, archaeology, architecture, conservation, project analysis and finance. Nominations for the 7 Most Endangered Programme 2023 were submitted by member organisations, associate organisations or individual members of Europa Nostra from all over Europe as well as by members of the European Heritage Alliance. For the Partisan Monument in Mostar a support was given among others also by Architectuul and DESSA Gallery from Ljubljana.
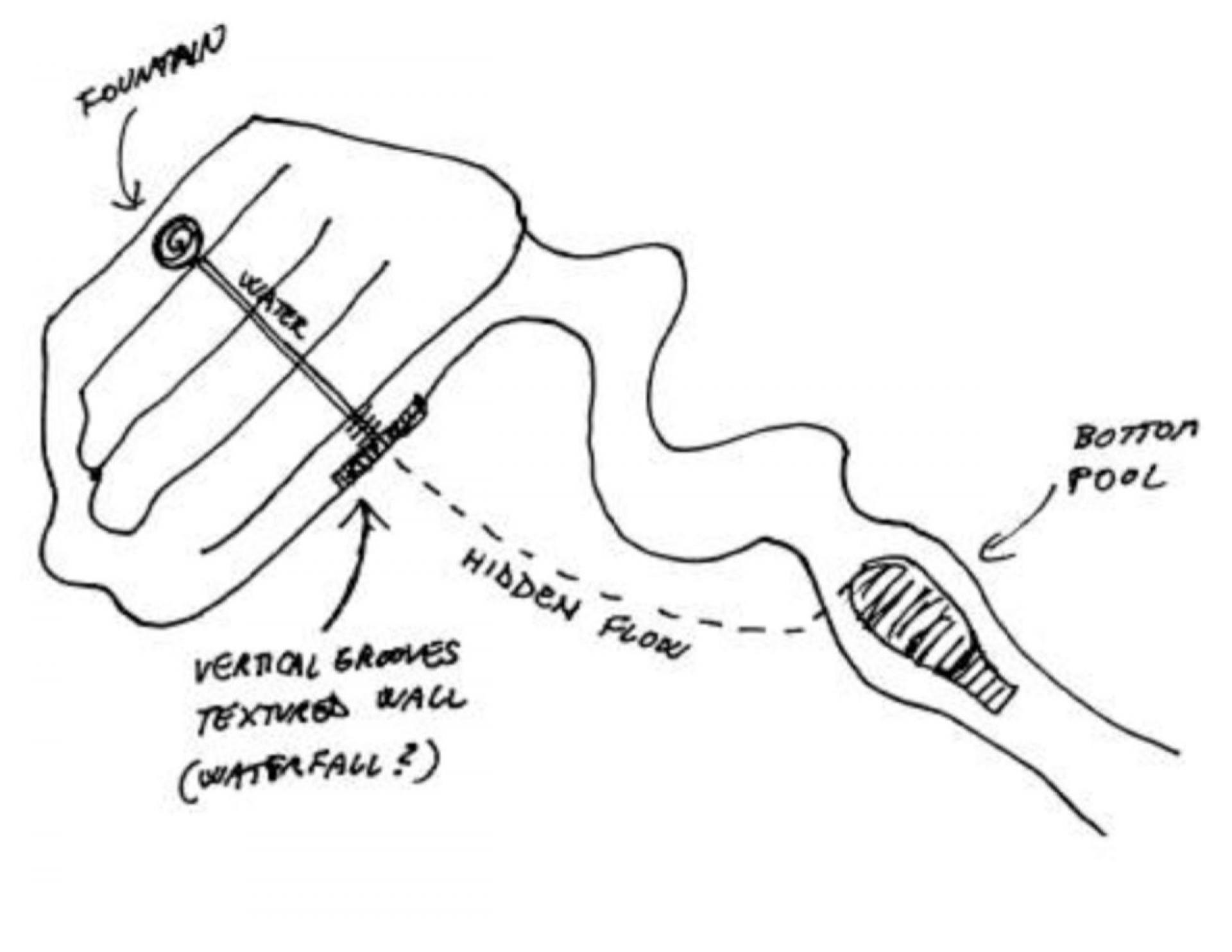
A sketch showing the path of the water flow.
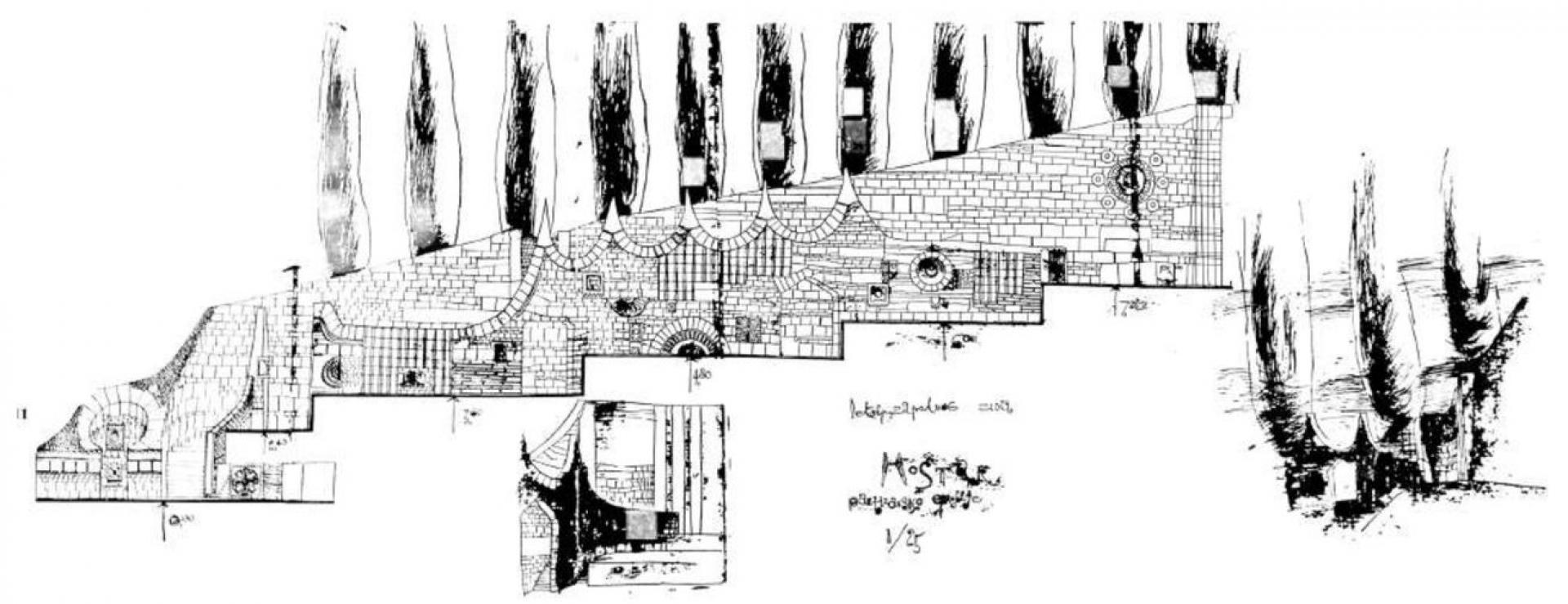
A cross-section of the cemetery and its terraces.
The Partisan Memorial Cemetery was built in 1965 in the town of Mostar. It is one of the largest anti-fascist monuments and sites in the Balkans, with its 300-metre-long paved ceremonial pathway rising more than 20 metres up a hill. The cemetery, which features some 700 individual tombstones as grave markers of freedom fighters from the Yugoslav Partisan movement, is part of a series of monuments and sites built in the region in memory of the partisans who died during World War II.
It was designed by the famous Yugoslav architect Professor Bogdan Bogdanović from Belgrade. Skilled stonemasons built the monument over several years, using over 12,000 carved limestone pieces, rubble from the town’s destruction during the war, and traditional stone roof tiles recycled from Mostar houses. The monument was inaugurated in 1965 by the President of Yugoslavia, Josip Broz Tito, on the occasion of the 20th anniversary of the liberation of Mostar from the Nazis and their local allies in 1945.
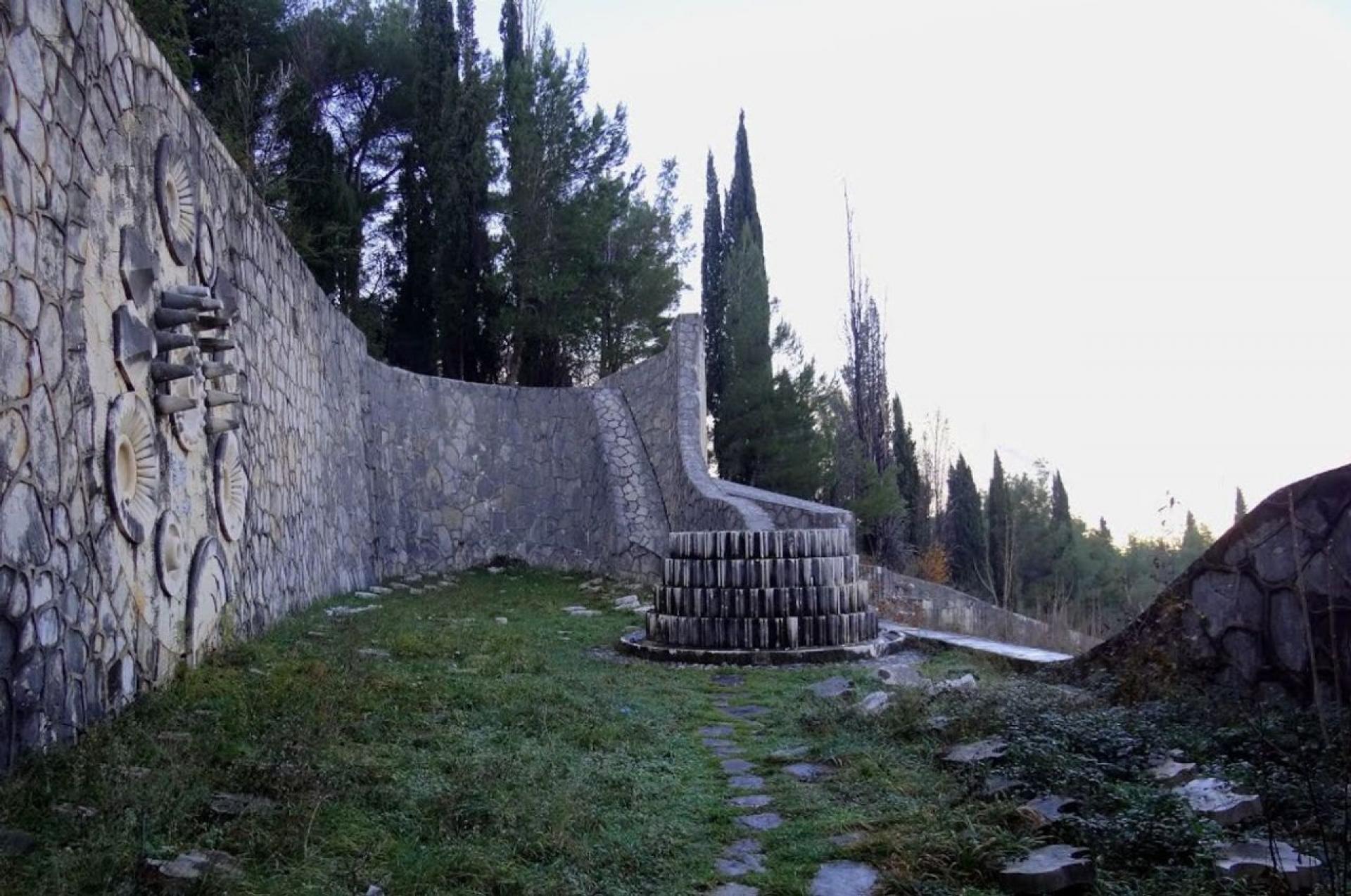

In front of the portal lies an a-centrically located gear-shaped fountain which used to develop a water stream that flowed down the terraces and emerged again in the dead end space at the bottom of the complex.
The Partisan Memorial Cemetery – with its memorial significance and relevance – has become a target for destruction, both in times of war and in times of peace. Although much damaged during the war in 1992-1995, the Partisan Memorial Cemetery suffered further damage in the period following the war. It is important to add that after the violent disintegration of Yugoslavia, many memorial sites built after World War II were neglected or even abandoned in the wider region, including the Partisan Memorial Cemetery in Mostar.
After the war, the first conservation and restoration works on the Partisan Memorial Cemetery were done in 2005 with the support of donor funds from the Government of The Netherlands and the Kingdom of Norway, and with co-financing from the City of Mostar and Federation of Bosnia and Herzegovina.
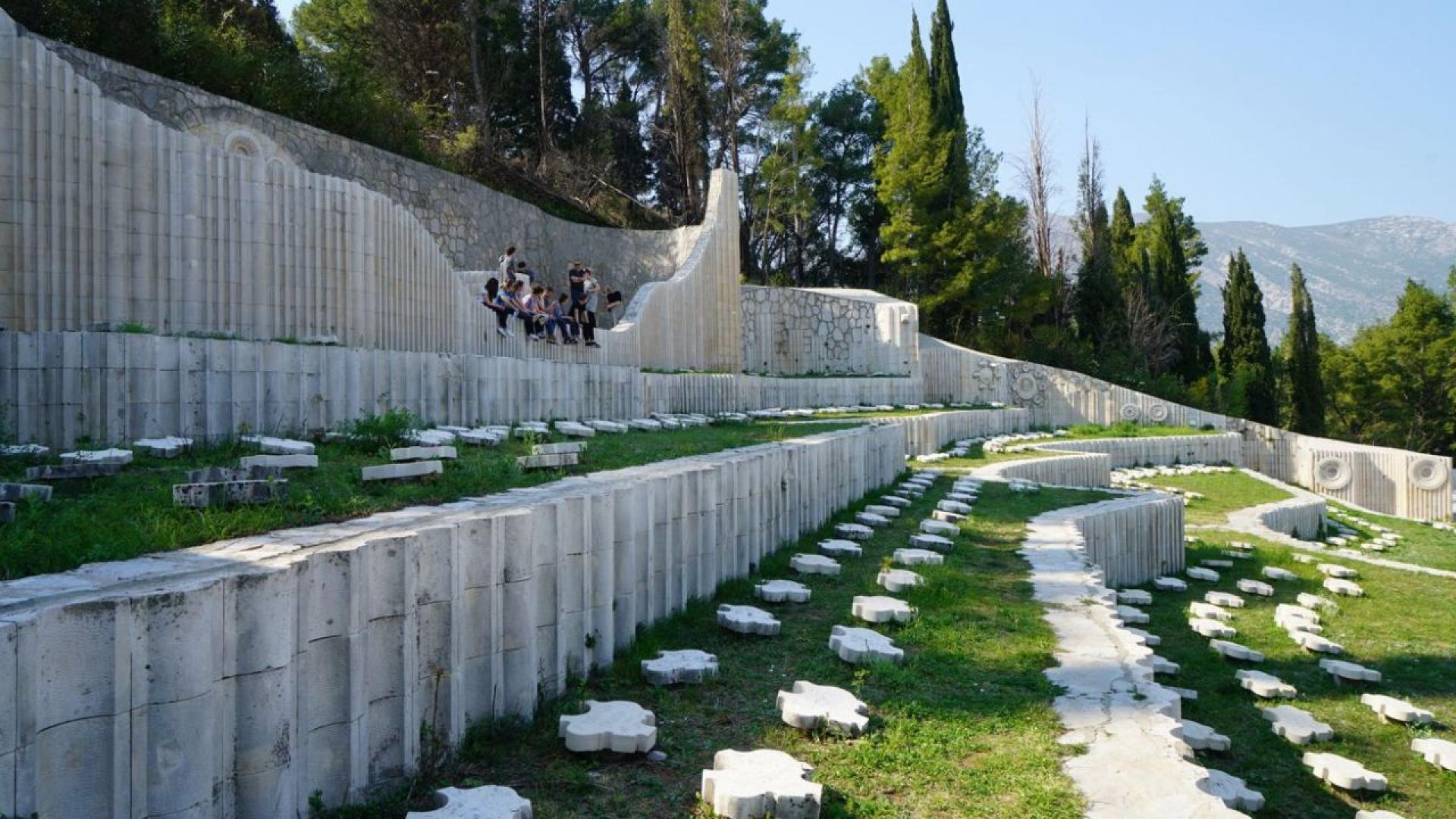

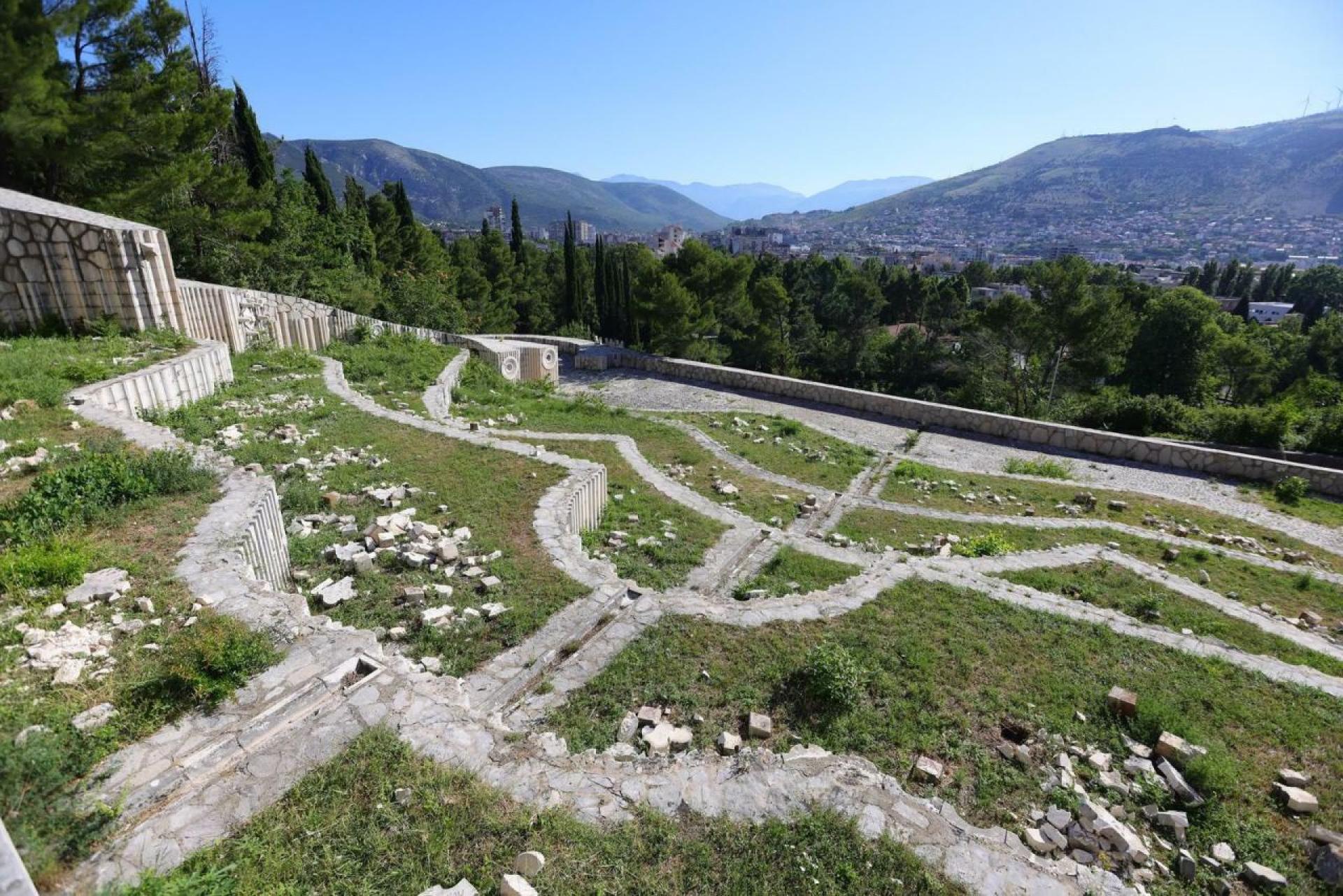
The complex is a necropolis, 630 abstractly shaped stone markers testify the multiethnic army that fought together and is buried here with names belonging to Serbs, Croats, Bosniaks, Jews.
However, the Partisan Memorial Cemetery has been, and still is, one of the region’s contested heritage sites. This has resulted in repeated acts of vandalism up until the most recent destruction which happened in June of 2022. This was followed by numerous reactions from the Mayor, the City Council, the Commission to preserve national monuments of Bosnia and Herzegovina, as well as from anti-fascist activists and associations both at local and international level, and also the reaction from numerous organisations from the territory of former Yugoslavia, which condemned the vandalism of the Partisan Memorial Cemetery. Recently, the Agency “Old City” of the City of Mostar launched the public procurement for the revitalisation, rehabilitation and illumination of the Partisan Memorial Cemetery. However, the monument does not yet have a holistic plan for its conservation and maintenance with a corresponding funding. The whole process of its necessary restoration and revitalisation therefore remains precarious.
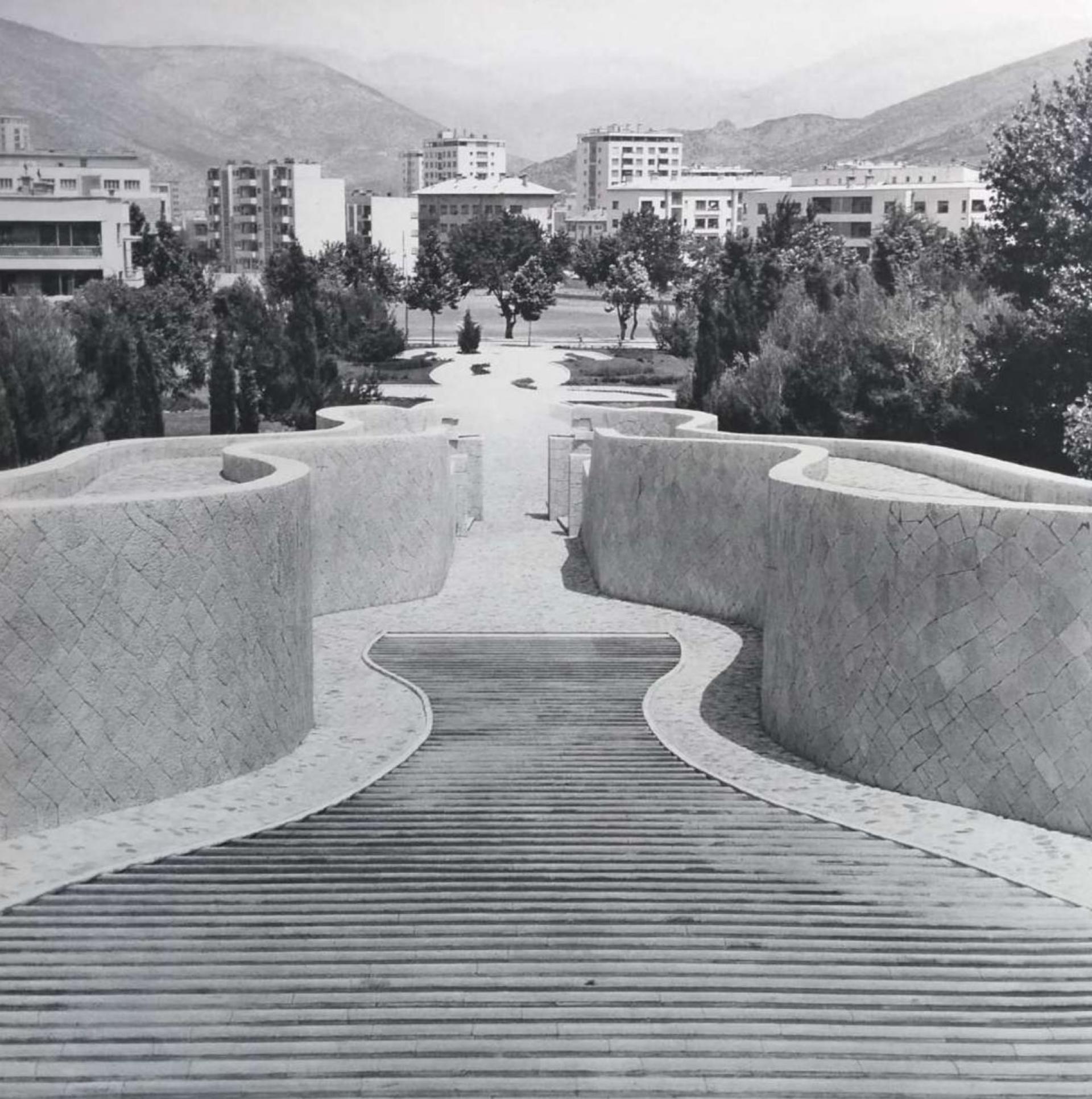

The partisan cemetery in Mostar is an integral part of the city and can be easily considered as an urban place.
The local community in Mostar has developed various campaigns for the legal protection of the Partisan Memorial Cemetery as a Monument of National Importance. Among other initiatives, they produced a documentary about the history of this memorial site and the threats and challenges it faces today.
The nomination of the cemetery to the 7 Most Endangered Programme 2023 was made by IDEAA Mostar with the endorsement of the Mayor of Mostar, the Galerija DESSA, Arcihtectuul and Europa Nostra Serbia. The nominator advocates for adequate legal protection of the Partisan Memorial Cemetery following its designation as a Monument of National Importance back in January 2006, for the European and international recognition of its outstanding historical and artistic values, as well as for the development of a sustainable rehabilitation, maintenance and management plan for this exceptional memorial site and the allocation of necessary funds – from local, national and European sources – for the quality implementation of such a comprehensive plan.
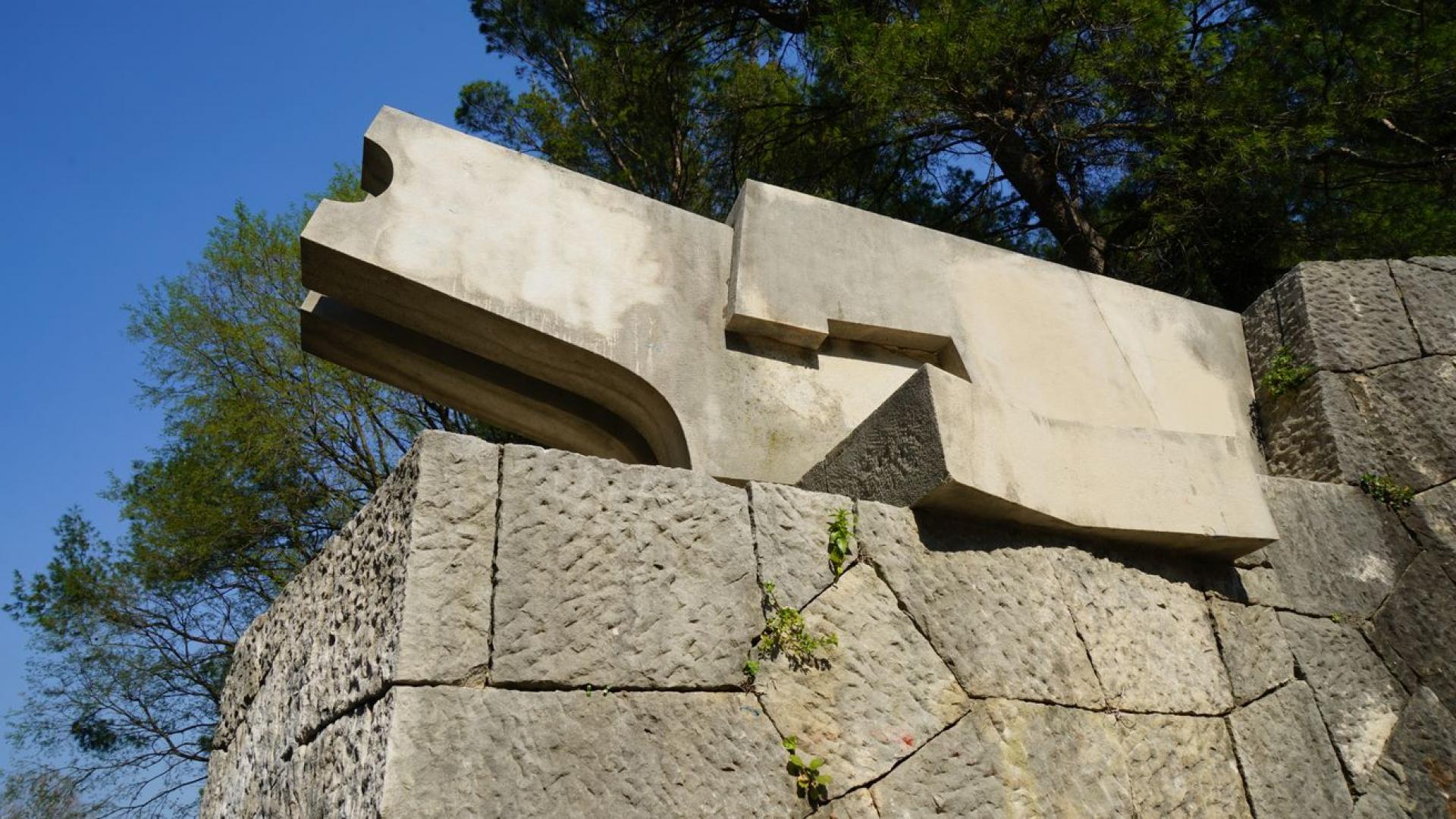

An abstract lion sculpture at the entrance of the complex.
The Advisory Panel of the 7 Most Endangered Programme commented: “The original design of the Partisan Memorial Cemetery in Mostar deliberately avoids the use of political or religious symbolism but makes use of cosmological symbols reminiscent of pre-Columbian remains and perhaps also referencing similar elements present in medieval sites in Bosnia and Herzegovina. As such, it is an outstanding example of the high-quality commemorative culture rooted in anti-fascist ideals within SFR Yugoslavia. At the time when Europe seeks to assert and put a much stronger emphasis on the vital importance of the shared values which form the very basis of the entire European project, this significant place of memory located in the Western Balkans should be restored with the support of local, national and European funds and protected for present and future generations.”

On Wednesday, June 15, 2022, vandals carefully and cold-bloodedly destroyed all the commemorative plaques.
The Executive President of Europa Nostra, Prof. Dr. Hermann Parzinger, stated: “This shortlist covers a wide variety of monuments and heritage sites which are facing different types of serious threats. The local communities and civil society organisations are deeply committed to preserving these remarkable examples of our shared heritage, but they need broader support. We therefore call on local, regional, national and European stakeholders, both public and private, to join forces with Europa Nostra and our network of members and partners to secure a viable future for these shortlisted sites.”
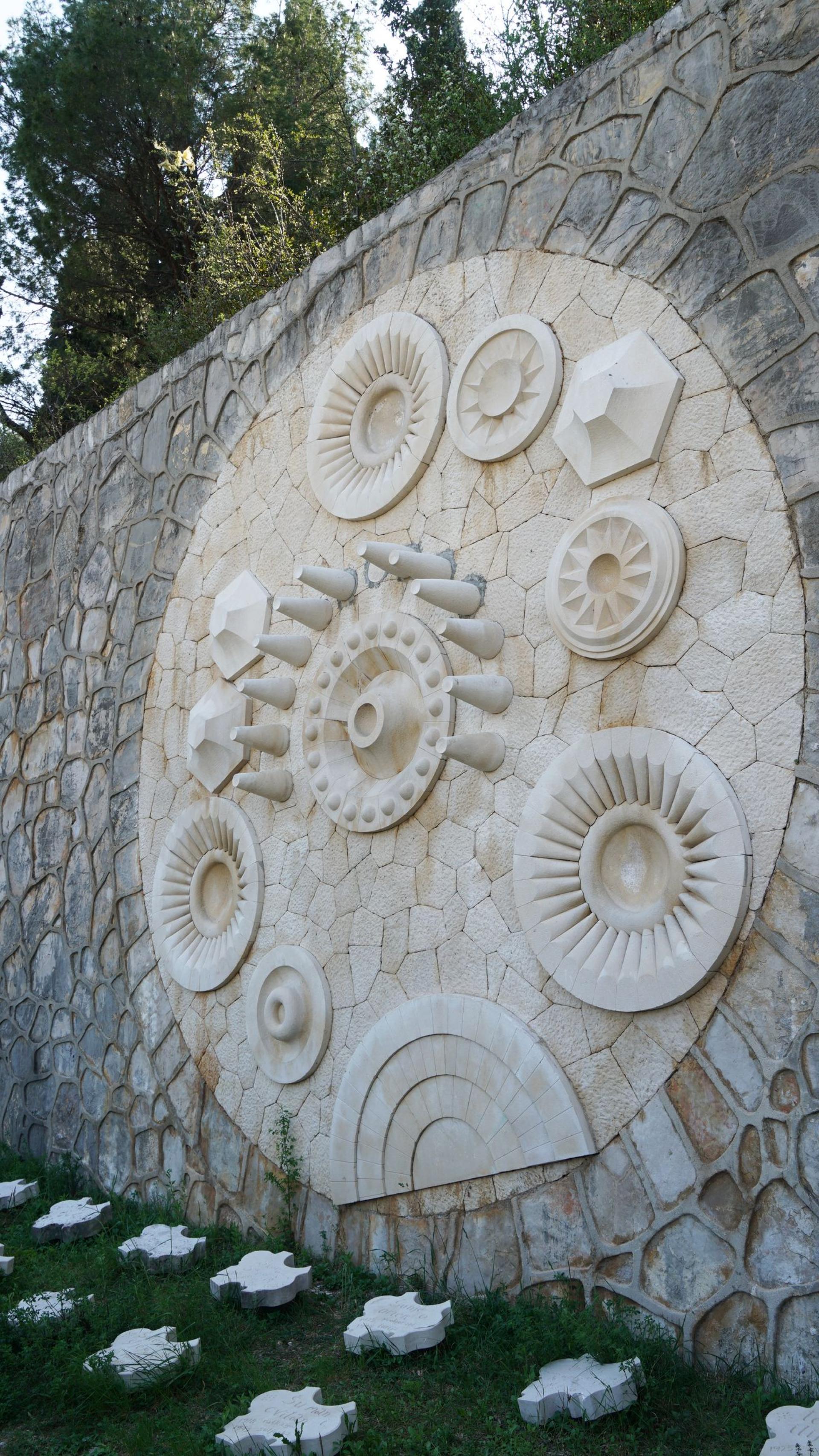

The "cosmic portal" is centrally located on the wall that backs the uppermost terrace. This circular element seems to act as a door between the two worlds and tries to reconcile the different visions that various religions have developed about the afterlife.
The final list of 7 Most Endangered heritage sites in Europe for 2023 will be unveiled in April.